Revving Up the Car Making Adventure!
Tapas Education, found at https://tapaseducation.com/, is an educational institution dedicated to fostering innovation and experiential learning. With a profound commitment to innovative projects, Tapas Education provides students with hands-on opportunities to explore cutting-edge concepts and technologies. Through a dynamic curriculum and real-world applications, Tapas Education empowers students to become forward-thinking problem solvers, preparing them for a future where creativity and innovation are paramount. Explore Tapas Education’s initiatives and witness the transformative power of education that extends beyond the classroom.
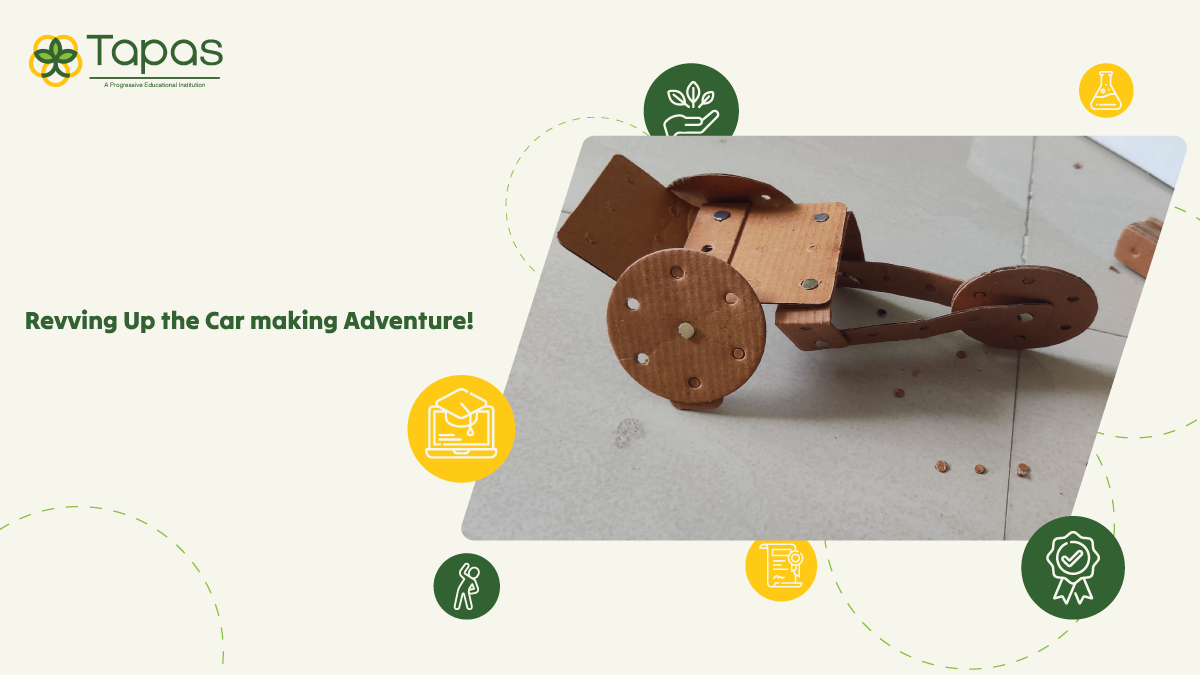
The Car-making Project at Tapas Education represents the epitome of classroom learning applied to real-world challenges. It offers students the chance to bridge theory and practice, transforming textbook knowledge into tangible solutions. By designing and building cars, students gain invaluable insights into sustainable transportation technology, problem-solving, and teamwork. This hands-on experience equips them with practical skills that extend far beyond the classroom, preparing them for careers in the ever-evolving field of hybrid and electric vehicles. The Car-making Project exemplifies how education at Tapas Education goes beyond theoretical understanding, empowering students to make a meaningful impact in the world.
THE PURPOSE
The educational goals and objectives behind initiating the Car-making Project encompass a comprehensive understanding of various scientific concepts while fostering critical skills in students:
Forces and Motion:
- Pushes and Pulls: To introduce students to fundamental concepts of forces and motion, emphasizing how these principles apply in real-world scenarios.
- Exploring How Toys Work: Encouraging hands-on exploration of how toys utilize forces for movement and operation.
- Observing Forces Around Us: Identifying and comprehending the role of forces in everyday life, from simple actions to complex mechanisms.
- Changing Movement: Understanding how forces can alter the trajectory and characteristics of motion.
- Utilizing Forcemeters: Developing skills in measuring forces and quantifying their impact.
- Friction: Gaining insights into the concept of friction and how it influences motion.
- Magnetic Materials: Exploring the relationship between magnetism and motion.
- Gravity: Understanding the fundamental force of gravity and its effects on objects.
Electricity:
- Understanding Electricity: Introducing students to the basics of electricity, its presence in our surroundings, and its safety considerations.
- Creating Circuits: Encouraging students to design and construct circuits, fostering a practical understanding of electrical flow.
- Using Motors and Buzzers: Applying electrical principles to create functional devices like motors and buzzers.
- Switches: Teaching the significance of switches in controlling the flow of electricity.
- Safety Awareness: Promoting a sense of responsibility and safety when dealing with electrical components.
By integrating these objectives into the Car-making Project, students not only gain a multidisciplinary understanding of science but also develop critical thinking, problem-solving, and practical skills essential for their educational and personal growth.
Project Flow:
The educational project at Tapas Education follows a structured and engaging flow to empower children with hands-on learning experiences that foster their understanding of forces and motion while promoting sustainability through recycling. Here’s a breakdown of the project’s key steps:
- Recycled Car Creation (Hands-On):
- Children kick off the project by creating their own miniature cars using recycled materials commonly found at home, such as plastic bottles and tissue paper rolls.
- This hands-on activity encourages creativity and resourcefulness, instilling the importance of sustainability from the outset.
- Questioning and Exploration:
- The project prompts children to think critically about what will propel their homemade cars.
- They explore the concept of forces and are encouraged to identify one of the fundamental forces (e.g., push, pull, or gravity) that can be harnessed to set their cars in motion.
- Children also learn about the control parameters required to effectively utilize a specific force.
- Mini Lessons and Practical Application:
- Through mini-lessons and interactive projects, children delve deeper into the understanding of various forces, including friction, magnetism, and more.
- These lessons provide a theoretical foundation, ensuring that children grasp the principles behind force and motion.
- Application to Car Building:
- Armed with their newfound knowledge, children apply what they’ve learned about forces to their homemade cars.
- They design and modify their cars, incorporating the control parameters learned earlier, to optimize their vehicles for motion.
- Testing and Analysis:
- The culmination of the project involves testing the functionality of the recycled cars.
- Children experiment with different forces, applying them to their cars and observing the results.
- They collect data and analyze the performance of each force application to draw conclusions.
Outcome:
Through this project, children gain a multifaceted learning experience that combines creativity, critical thinking, and scientific principles. They not only acquire a deeper understanding of forces but also develop an appreciation for recycling and sustainable practices. By comparing results and making informed decisions about which force best propels their cars, they apply their newfound knowledge in a practical context.
Table: Comparison of Forces Applied to Recycled Cars
| FORCE TYPE | PERFORMANCE EVALUATION | CONCLUSION |
| Push | ||
| Pull | ||
| Gravity | ||
| Friction | ||
| Magnetism | ||
| Elasticity |
In the table, children record their observations and evaluations for each force type applied to their cars, ultimately arriving at a conclusion about the most effective force for propelling their recycled vehicles. This project not only enhances their scientific knowledge but also fosters critical thinking and environmental consciousness.
In conclusion….
The Car-making Project at Tapas Education offers a dynamic and engaging learning experience for children. Through hands-on creation, critical thinking, and practical application of scientific concepts, students are not only building recycled cars but also expanding their understanding of forces and motion. The project encourages sustainability and resourcefulness from the very start.
As part of this educational journey, children have been prompted to explore the forces that drive motion and apply this knowledge to their homemade cars. Mini lessons and interactive projects have enriched their theoretical foundation, and they’ve harnessed this understanding to optimize their vehicle designs. The testing and analysis phase empowers them to make informed decisions about which force best suits their cars.
The next step for the young scientists is to finalize their findings and submit their reports. We invite you to explore their discoveries and insights in greater detail on our website: Tapas Education – Car-making Project. By doing so, you’ll not only witness the fruits of their labor but also support their educational journey.
Join us in celebrating the innovation, creativity, and environmental consciousness of these young minds. Let’s inspire the scientists of tomorrow to drive positive change today. Visit our website now and be a part of their journey!
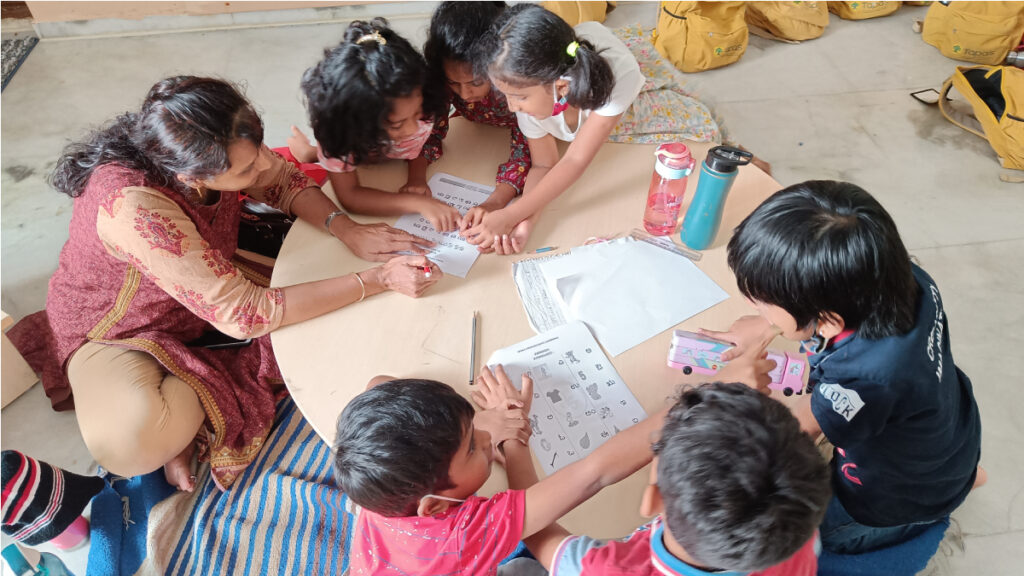
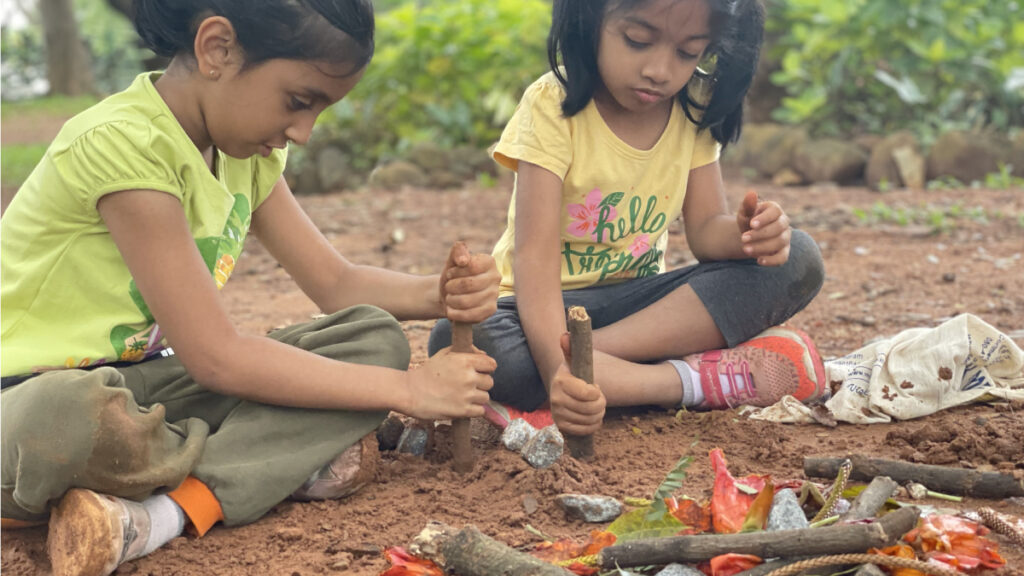
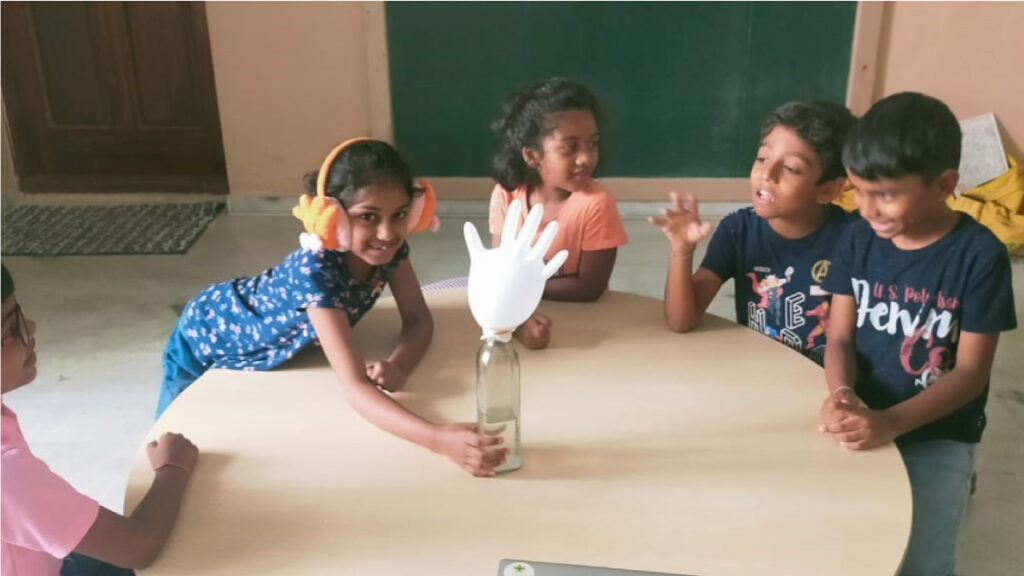








 Each project is looked at minutely and in convergence with the student mix and their interests, behaviours and attention levels to bring about the maximum result. There are many different types of programs and curriculums that PBL follows. At the beginning of the semester, the educator sets the goals that they need to target, focus on and achieve cumulatively. Changes that concentrate on growth, however small they may be, but well-orchestrated are made and these bring about a flurry of change in the classroom in the correct manner.
Each project is looked at minutely and in convergence with the student mix and their interests, behaviours and attention levels to bring about the maximum result. There are many different types of programs and curriculums that PBL follows. At the beginning of the semester, the educator sets the goals that they need to target, focus on and achieve cumulatively. Changes that concentrate on growth, however small they may be, but well-orchestrated are made and these bring about a flurry of change in the classroom in the correct manner.

 Education should not be limited to the four walls of classrooms and as educators, it is our responsibility to create adults who are equipped with skills and resources to thrive in a constantly changing work environment, who are able to live a fulfilling life and be active contributors to society. Tapas, a 100%
Education should not be limited to the four walls of classrooms and as educators, it is our responsibility to create adults who are equipped with skills and resources to thrive in a constantly changing work environment, who are able to live a fulfilling life and be active contributors to society. Tapas, a 100% 

